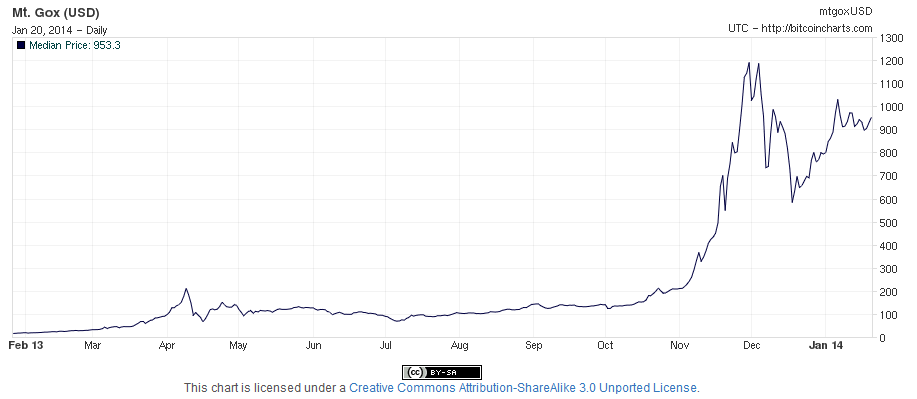
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, the popularity of which over the past few years has increased due to the incredible growth rate, which did not escape the attention of the public and the media. Bitcoin remains a very attractive currency for both ordinary users and cybercriminals. Malware developers, like ordinary criminals, always come running to the smell of money, so today cryptocurrency has become a concept that is fashionable in cyberspace.
Since such a currency is not controlled by the governments, but by the creators, some authorities noticeably became nervous about what caused the heated debate about whether to regulate the issue and the turnover of bitcoins. But this is actually not so easy, given the very idea of bitcoins and the peculiarities of the cryptocurrency distribution network, which were well thought out by the creator Satoshi Nakamoto. In 2010, he left the project, leaving no trace behind, thanks to which both his personality and the fruit of his work were overgrown with mysticism and legends. In any case, we know for sure that even after several years, Bitcoin is stronger than ever and the number of its adherents around the world continues to increase every day.
In addition, the very nature of digital currencies has many advantages over real counterparts. Cryptocurrency-based payment systems are fast (transaction verification only takes about ten minutes) and cheap (you no longer need to pay for processing by credit organizations). If we add to this the decentralization, confidentiality and widespread availability of currency, then the desire to invest time and money in Bitcoins is understandable.
Initially, the most common way of earning bitcoins was a process called “mining”, during which the user “swapped” the computing power of a CPU or GPU for bitcoin shares (depending on a number of factors). Since at that time the number of miners was small, it was a cost-effective solution and the best way to invest in a new currency without much fuss. Mining is an integral part of the Bitcoin payment security scheme, as it serves to verify network operations, preventing Double Spending attacks, the purpose of which is to carry out a second payment, when the same bitcoins are translated twice to different people.
Moreover, having appreciated the benefits of using new currency, many of the first miners began to create mining installations (computers), computers fully adapted for the production of cryptocurrency. Since the miner, who is the fastest to solve the crypto task, provided by the network, receives a bitcoin reward, the real race of the creators of the most powerful mining computers has begun. The cost of such specialized equipment is quite high (usually in such a PC there are several powerful high-end video cards working in conjunction), but at that time the payback period justified such a significant investment, so many people without hesitation joined the mining. After the GPU as a tool for mining was supplanted by the emerged specialized integrated circuits (ASIC), many enthusiasts and small companies began to build their own mining farms, thus ousting little players from the market.
One of the most popular ways to get Bitcoin today is to visit special trading sites where you can quickly and safely exchange your currency for Bitcoins. In addition, many online merchants started accepting bitcoins when paying for goods or services, which demonstrates the real importance of cryptocurrency. One of the most famous (and at the same time illegal) sites working with bitcoins was the notorious Silk Road resource, which was part of the “shadow Internet”: there the customers were offered the widest range of prohibited substances and illegal services. Although Bitcoin as a currency is not completely anonymous, it provides a certain degree of confidentiality, which is unthinkable for other payment options, so the cryptocurrency has become a profitable alternative to money in the world of cybercriminals.
“The most fertile ground for bitcoins is such countries as Cyprus, Argentina, China, and others affected by financial turmoil or characterized by tight financial regulation” – Garrick Heilman, an expert on the history of economics at the London School of Economics.
But if everything happens in a virtual environment, where to store hard earned crypto-money? As in real life, you will need a wallet. In response to the growing need of users to securely store their bitcoins, a number of online wallets have appeared. Unfortunately, such services do not guarantee one hundred percent safety of funds: the recent robbery of a popular Bitcoin-bank has led some users to lose savings totaling the equivalent of $ 1.2 million. Of course, you can store cryptocurrency not on the Internet, using free and widely used tools, but take care of creating a backup copy of your wallet so that all your savings will not be spent on any online garbage dump. For example, such a nuisance occurred with James Howells, who threw out the old drive, where his wallet was stored with about 7,500 Bitcoins, which today is 4 million pounds sterling.
However, there is one drawback in using Bitcoins in modern financial transactions, and this is what all transactions made with Bitcoins are irreversible. Of course, some supporters of cryptocurrency consider this an advantage, but in order to become a mature and stable currency, Bitcoin must provide the means to protect users from fraud and theft. In addition, given the high volatility of the cryptocurrency rate, people owning Bitcoins have to spend them pretty quickly, until the rate drops again. So, at present, bitcoins are not a suitable currency for storing pension savings, and therefore they should be actively spent where they no longer accept any other forms of payment. Perhaps the emergence of a new Canadian “ATM” for bitcoins (which has already been dubbed “Robokoyin”) will allow a less IT-savvy audience to try out this currency for everyday transactions.
The number of types of malware associated with Bitcoins is growing day after day: you can quite often meet Trojans distributed via Skype, mining botnets and other complex threats that are now equipped with mining capabilities. But the actions of cybercriminals are no longer limited to the development and distribution of malicious software: today they already offer illegal services and products on the shadow Internet. In most cases, the payment is made in Bitcoins, since both parties to the transaction can thus keep the secret of the individual in carrying out illegal activities. Silk Road may have been closed, but with the advent of a huge number of websites every day, the cryptocurrency will remain highly demanded by both criminals and regular users.